从 MongoDB 迁移到 ProtonBase 指南
本文为您介绍如何从 Mongo 迁移至 Protonbase。
背景信息
MongoDB 是一种文档数据库,它所具备的可扩展性和灵活性可以满足您对查询和索引的需求,详情请参见 MongoDB 是什么? (opens in a new tab)
下表为您介绍 MongoDB 数据库中的重要概念。
| 概念 | 描述 |
| Database | 相当于 Schema。Mongodb 数据库中可以存在多个 Database,一个 Database 中可以存在多个 Collection。 |
| Collection | MongoDB在collections中存储文档(documents)。Collections类似于关系型数据库中的表(tables)。 |
| Document | MongoDB的文件是由field和value对的结构组成,类似于行的记录。 |
准备工作
网络
参考 数据同步网络配置
权限
- 简单赋权,可以到Database级,赋权了后,批量读和changeStream流式读都可以
use test;
db.createUser({
user: "protonbase",
pwd: "xxxxxx",
roles: [
{
role: "read",
db: "test",
}
]
});- 复杂赋权,可以到具体的collection和操作
use test;
db.createRole({
role: "readAndWatchSpecificCollection",
privileges: [
{
resource: { db: "test", collection: "a" },
actions: ["find", "changeStream"]
}
],
roles: []
});
db.createUser({
user: "protonbase",
pwd: "xxxxx",
roles: [
{ role: "readAndWatchSpecificCollection", db: "test" }
]
});数据同步
1.新建数据迁移任务。
- 登录protonbase控制台ProtonBase (opens in a new tab)。并进入到相应的data center
- 在左侧导航栏,单击 数据同步 --> 数据导入。
- 在 数据导入 页面,单击右上角的 + 数据导入作业。
2.在 选择源和目标 页面,配置各项参数。
| 参数 | 描述 |
| 作业名 | 建议数字和字母的组合。 |
| 源端 | 选择MongoDB |
单击 确定。在 编辑 页面,配置各项参数。
MongoDB:
| 参数 | 描述 |
| 连接方式 | 直接连接需要源端配置公网访问,并且将teleport的ip加入到白名单。 Tunnel参考网络配置 |
| 域名[:端口] | 数据库连接信息,包括端口,类似mongodbserver1:27017,mongodbserver2:27018,mongodbserver3:27019 |
| 用户名 | 用于同步的用户名,需要参考准备工作中的权限设置 |
| 密码 | 用户的密码 |
| Auth Source | 用于进行身份验证的数据库 |
| Replica Set | 副本集名 (opens in a new tab) |
| Read Preference | 设置的读策略 (opens in a new tab) |
| Read Concern | 设置的读关注 (opens in a new tab) |
ProtonBase
| 参数 | 描述 |
| 连接方式 | 可以直接选择当前data center内的warebase或者通过域名端口方式访问其他区域的warebase |
| WareBase | 选择需要同步的WareBase |
| 用户 | 用于同步的用户 |
配置完上述过程后,需要确定teleport能够连接到数据源及目标端,可以通过teleport页面的连接测试功能测试网络连接。
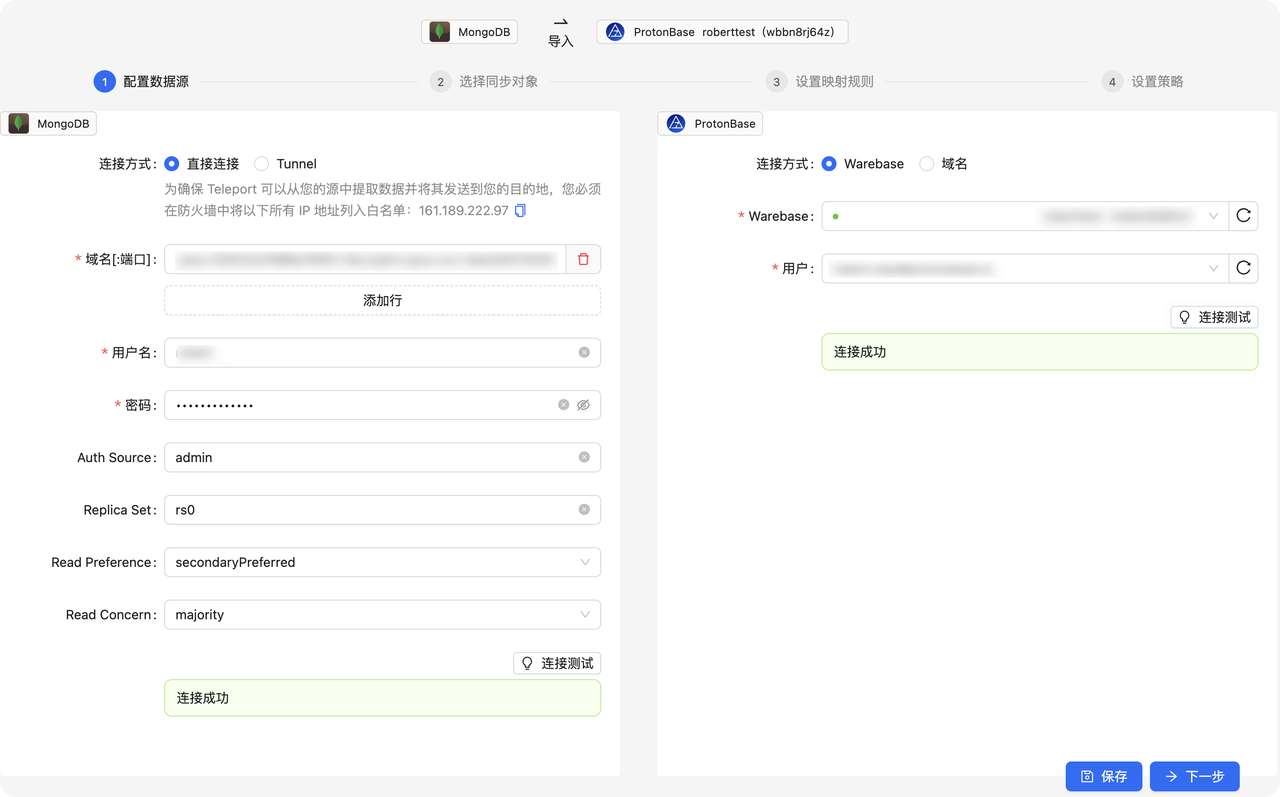
3. 在 选择同步对象 页面,选择需要同步的数据库。可以配置同步的如下配置,参考同步对象筛选
| 参数 | 描述 |
| 对象类型 | 需要同步的对象类型,默认同步Collection |
| 同步所需的DDL 操作 | 允许同步的DDL 操作 |
| 同步所需的DML 操作 | 允许同步的DDL 操作 |
| 目标表类型 | 可以配置默认目标端的表的存储类型,具体可以参考表结构设计 |
| 同步外键 | 是否同步外键,MongoDB忽略该选项 |
| 同步索引 | 是否同步索引 |
| 同步唯一索引 | 是否同步唯一索引 |
| Drop 策略 | 删除表的策略,包括 - RESTRICT,将会进行默认的drop操作。 - CASCADE,将会进行DROP CASCADE操作。 - RENAME,将会对目标表进行rename操作。 |
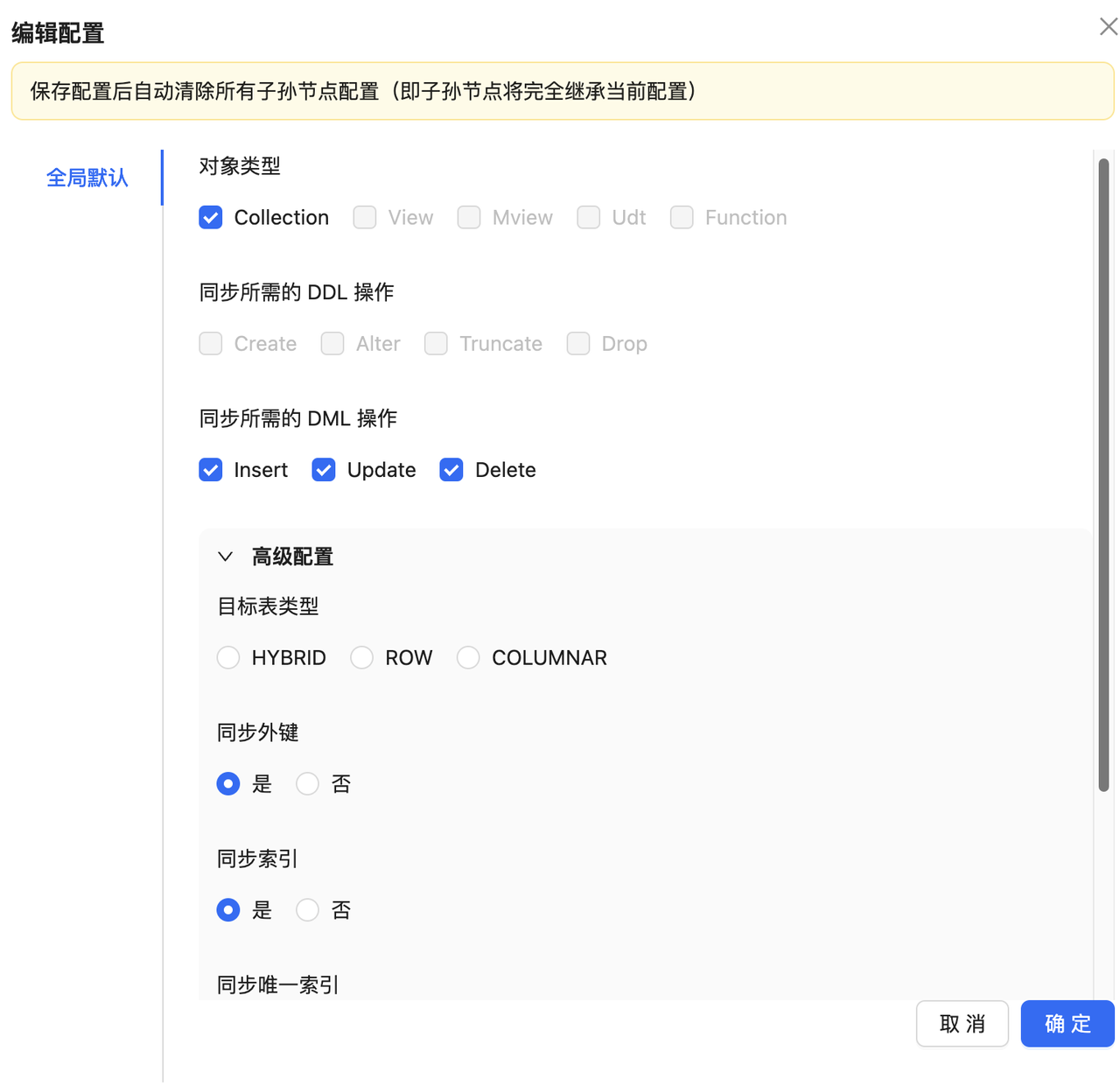
4. 在 设置映射规则 页面,查看映射规则及字段映射,参考 同步对象映射。
由于MongoDB存放的是json内容,可以在字段映射的时候修改字段映射规则

5. 在 设置策略 页面,查看数据同步模式及脏数据处理策略。
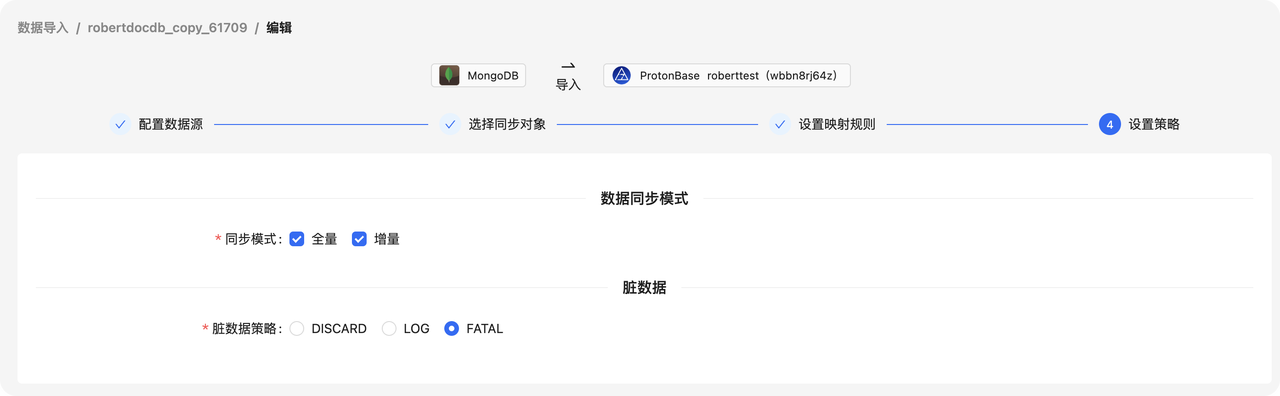
启动同步作业后,查看同步状态。

同步过程中的状态可以参考作业操作和状态
6. 检查数据情况。
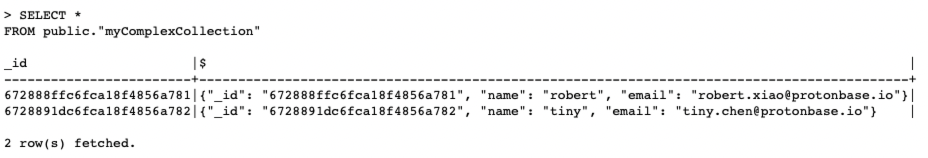
检查MongoDB的数据情况。
/* 1 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("672888ffc6fca18f4856a781"),
"name" : "robert",
"email" : "robert.xiao@protonbase.io"
}
/* 2 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("6728891dc6fca18f4856a782"),
"name" : "tiny",
"email" : "tiny.chen@protonbase.io"
}在MongoDB新增数据。
/* 1 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("672888ffc6fca18f4856a781"),
"name" : "robert",
"email" : "robert.xiao@protonbase.io"
}
/* 2 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("6728891dc6fca18f4856a782"),
"name" : "tiny",
"email" : "tiny.chen@protonbase.io"
}
/* 3 */
{
"_id" : ObjectId("6729c0a4c6fca18f4856a7c0"),
"name" : "eric",
"email" : "eric@protonbase.io"
}检查同步的数据。

应用改造示例
改造时需注意:
- 替换 MongoDB 驱动(如
mongodb-driver-sync)为 PostgreSQL 驱动(如org.postgresql.Driver)。 - 在应用中将 MongoDB 的集合操作改为对 PostgreSQL 表的操作。
- 如果使用 ORM 工具,推荐使用支持 PostgreSQL 的 ORM(如 Hibernate、Spring Data JPA 等)。
插入数据
MongoDB 示例(Java)
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection("users");
Document doc = new Document("name", "Alice")
.append("age", 25)
.append("city", "New York");
collection.insertOne(doc);PostgreSQL 示例(Java)
String query = "INSERT INTO users (name, age, city) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement(query)) {
stmt.setString(1, "Alice");
stmt.setInt(2, 25);
stmt.setString(3, "New York");
stmt.executeUpdate();
}查询数据
单条件查询
MongoDB 示例(Java)
Document query = new Document("name", "Alice");
Document result = collection.find(query).first();
if (result != null) {
System.out.println(result.toJson());
}PostgreSQL 示例(Java)
String query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = ?";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement(query)) {
stmt.setString(1, "Alice");
try (ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery()) {
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println("Name: " + rs.getString("name"));
System.out.println("Age: " + rs.getInt("age"));
System.out.println("City: " + rs.getString("city"));
}
}
}多条件查询
MongoDB 示例(Java)
Document query = new Document("age", new Document("$gte", 20))
.append("city", "New York");
FindIterable<Document> results = collection.find(query);
for (Document doc : results) {
System.out.println(doc.toJson());
}PostgreSQL 示例(Java)
String query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE age >= ? AND city = ?";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement(query)) {
stmt.setInt(1, 20);
stmt.setString(2, "New York");
try (ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery()) {
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println("Name: " + rs.getString("name"));
System.out.println("Age: " + rs.getInt("age"));
System.out.println("City: " + rs.getString("city"));
}
}
}更新数据
MongoDB 示例(Java)
Document query = new Document("name", "Alice");
Document update = new Document("$set", new Document("age", 26));
collection.updateOne(query, update);PostgreSQL 示例(Java)
String query = "UPDATE users SET age = ? WHERE name = ?";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement(query)) {
stmt.setInt(1, 26);
stmt.setString(2, "Alice");
stmt.executeUpdate();
}删除数据
MongoDB 示例(Java)
Document query = new Document("name", "Alice");
collection.deleteOne(query);PostgreSQL 示例(Java)
String query = "DELETE FROM users WHERE name = ?";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement(query)) {
stmt.setString(1, "Alice");
stmt.executeUpdate();
}聚合操作
MongoDB 示例(Java)
List<Bson> pipeline = Arrays.asList(
Aggregates.group("$city", Accumulators.sum("count", 1))
);
AggregateIterable<Document> results = collection.aggregate(pipeline);
for (Document doc : results) {
System.out.println(doc.toJson());
}PostgreSQL 示例(Java)
String query = "SELECT city, COUNT(*) AS count FROM users GROUP BY city";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement(query);
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery()) {
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println("City: " + rs.getString("city") + ", Count: " + rs.getInt("count"));
}
}常见问题与解决方法
数据模型设计差异
问题:MongoDB 的文档结构允许嵌套字段,PostgreSQL 中则需转换为多表结构或使用 JSON 类型字段。 解决方案:
- 如果嵌套层次简单,直接用 PostgreSQL 的
JSON或JSONB类型字段存储嵌套数据。 - 对复杂嵌套字段,设计关系型表结构,并通过外键关联实现。
示例: MongoDB 文档:
{ "name": "Alice", "orders": [{ "id": 1, "total": 50 }] }PostgreSQL 表:
CREATE TABLE users (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT);
CREATE TABLE orders (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, user_id INT, total NUMERIC, FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id));